Manage Security
Administrators and DataBlock Designers (with the right permissions) can configure the security for Argos objects. Users and/or groups can be granted or denied permissions as required.
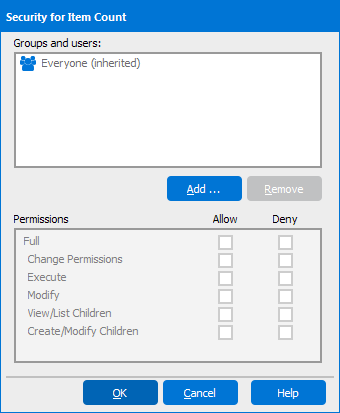
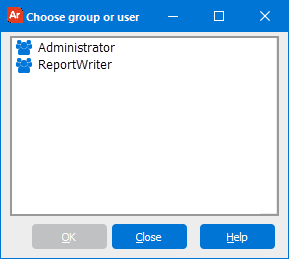
Select a user or group from the list and select OK to configure permissions, or click the Add. . . button to add a new user or group to the list:
You can Allow or Deny the permissions listed below:
- Full: Perform any action, including changing permissions for any user. Checking this option is the same as having all other options checked.
- Change Permissions: Modify permissions for any user. Note that this permission is the same in some respects as Full, since the user could easily enable the Full option if granted Change Permissions.
- Execute: Run the selected object.
- Modify: Modify and Run the selected object.
- View/List Children: View the object and the children of the object. Typically this permission would be placed on a folder or DataBlock to enable children of that object to be viewed.
- Create/Modify Children: Create or Modify child objects. This permission is often placed on a folder or DataBlock to allow children to be created.
To remove security for a user or group, select the user or group and click the Remove button. Note that they may still have permissions due to membership in other groups (see notes below).
For security purposes, schedules are considered part of the report that the schedule belongs to. When configuring security, keep in mind that users will need at least Create/Modify permissions on the parent report in order to edit a schedule. This is in addition to the Edit Schedule permission granted through the MAPS user roles.
Argos includes the following security features:
Direct Security: Security defined on the user level supersedes any permissions they may have due to settings on the group level. For example, if a user is Denied permission to Modify an object, they will not be able to do so even if one or more of their groups has this permission Allowed.
Inherited Security: Note that objects in Argos automatically 'inherit' the permissions of their parent. For example, if a folder has a set of permissions, all objects in that folder will have the same permissions unless overridden. This inheritance also extends to the objects' 'grandchildren', 'great grandchildren', etc.
Note also that users who have been granted Execute permission on a report are given Execute permission on the DataBlock linked with that report, since they cannot execute the report without also executing the DataBlock.
Accumulated Group Permissions: When a user attempts to access an Argos object, Argos will look at the permissions of all groups that they belong to. Argos grants the user all accumulated positive group permissions to the object (unless that user has been Denied permissions - see above). For example, if a user has been granted direct permission to Execute an object, and their membership in a group granted them permission to Modify the object, their accumulated positive permissions would be Execute and Modify. Even if the user was in a second group that was denied the ability to Modify the object, they would still be able to Modify the object due to their membership in the first group.
Everyone Group: Pay special attention to permissions granted to the Everyone group as all users are automatically members of this group. It is often a good policy to Deny permissions to the Everyone group once other groups have been made.